3D Classification
Contents
3D Classification#
Goal: To classify particles into 3D volumes and further refine those volumes to a higher resolution.
Introduction#
After generating your low resolution Ab Initio class(es), we can then perform a few different jobs to either refine A) multiple models; B) get rid of noise/junk particles; or C) refine a single model to higher resolution. To refine multiple models on Cryosparc, we can run a job called “Heterogeneous Refinement,” which will take a given particle stack and separate those particles into multiple volumes, which you will provide, and see which volume the particles fit best into. This can be helpful if you believe that your molecule has multiple conformations, to separate your particle stack into those conformations. It is also helpful for getting rid of noise, as particles that fit into “bad” volumes (or spheres), can be discarded. Finally, we can perform jobs such as “Homogeneous Refinement” or “Nonuniform Refinement” to further refine and define a resolution for a single volume and particle stack. In general, Nonuniform Refinement will work better and yield a higher resolution final volume for small particles, such as RNA, so it is preferable to use this job.
Cryosparc Heterogeneous Refinement#
Create the job “Heterogeneous Refinement”. In general, we keep parameters for this job at the defaults. For your inputs, you will use your particle stack as well one of these three options (or some combination of all three): 1) a “good” volume from Ab Initio as well as a “bad” volume; 2) a “good” volume from Ab Initio and a sphere; 3) multiple “good” volumes representing different potential conformations of the molecule.
Creating a Sphere
Below are the steps to create a sphere to use in heterogeneous refinement:
Open a “good” Ab Initio model in ChimeraX
In the command bar, type the following command:
volume scale #map factor 0
This will create a new volume which is empty but has the same dimensions as your Ab Initio volume. We will refer to this as map 2.
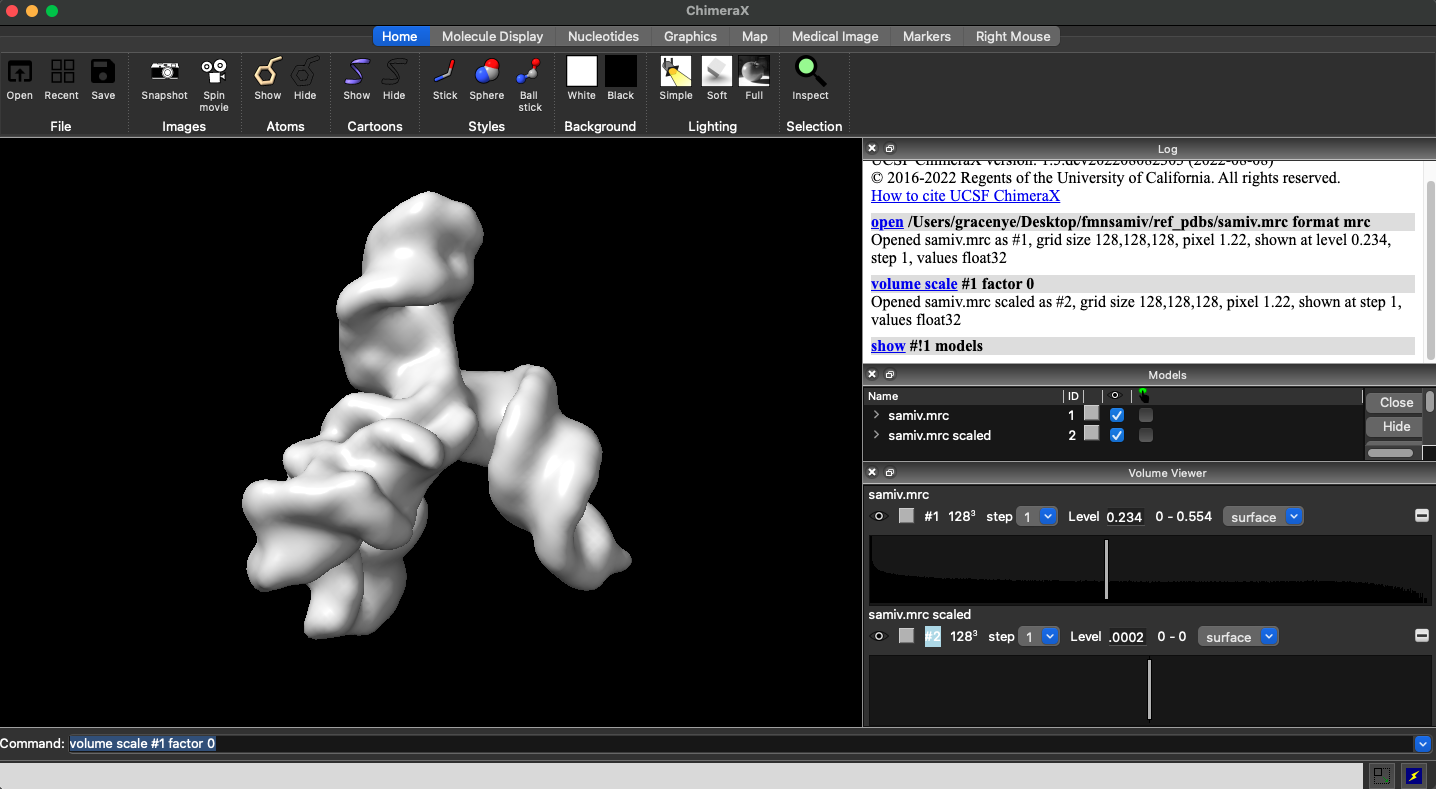
Now type in the following command:
volume scale #map2 shift 1
This will create a new volume with the same dimensions as the previous one, but it will contain a cube of size 1, which we shall refer to as map 3.
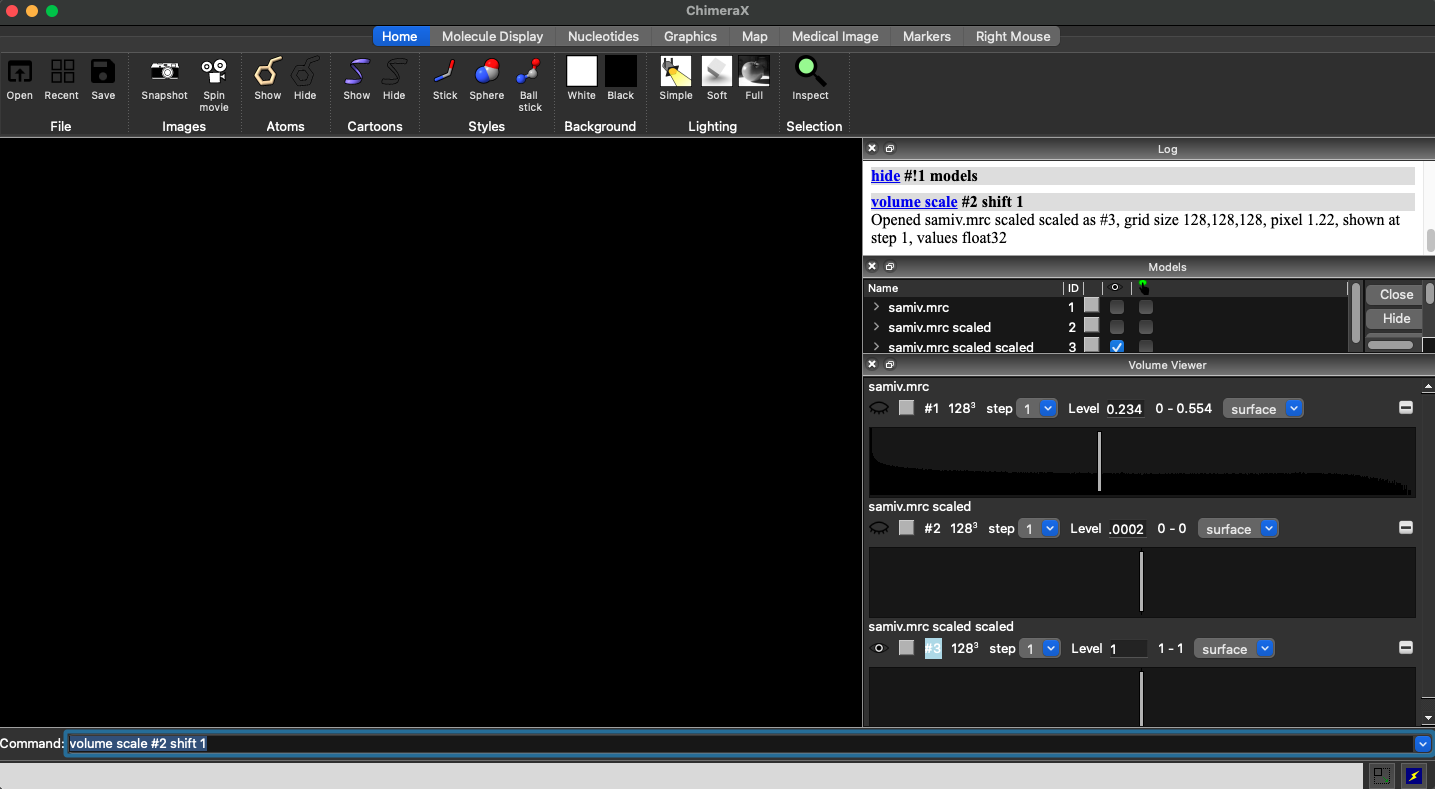
Now, with map 3 opened, select the “Tools” tab, then select “Volume Data”, and then “Map Eraser”.
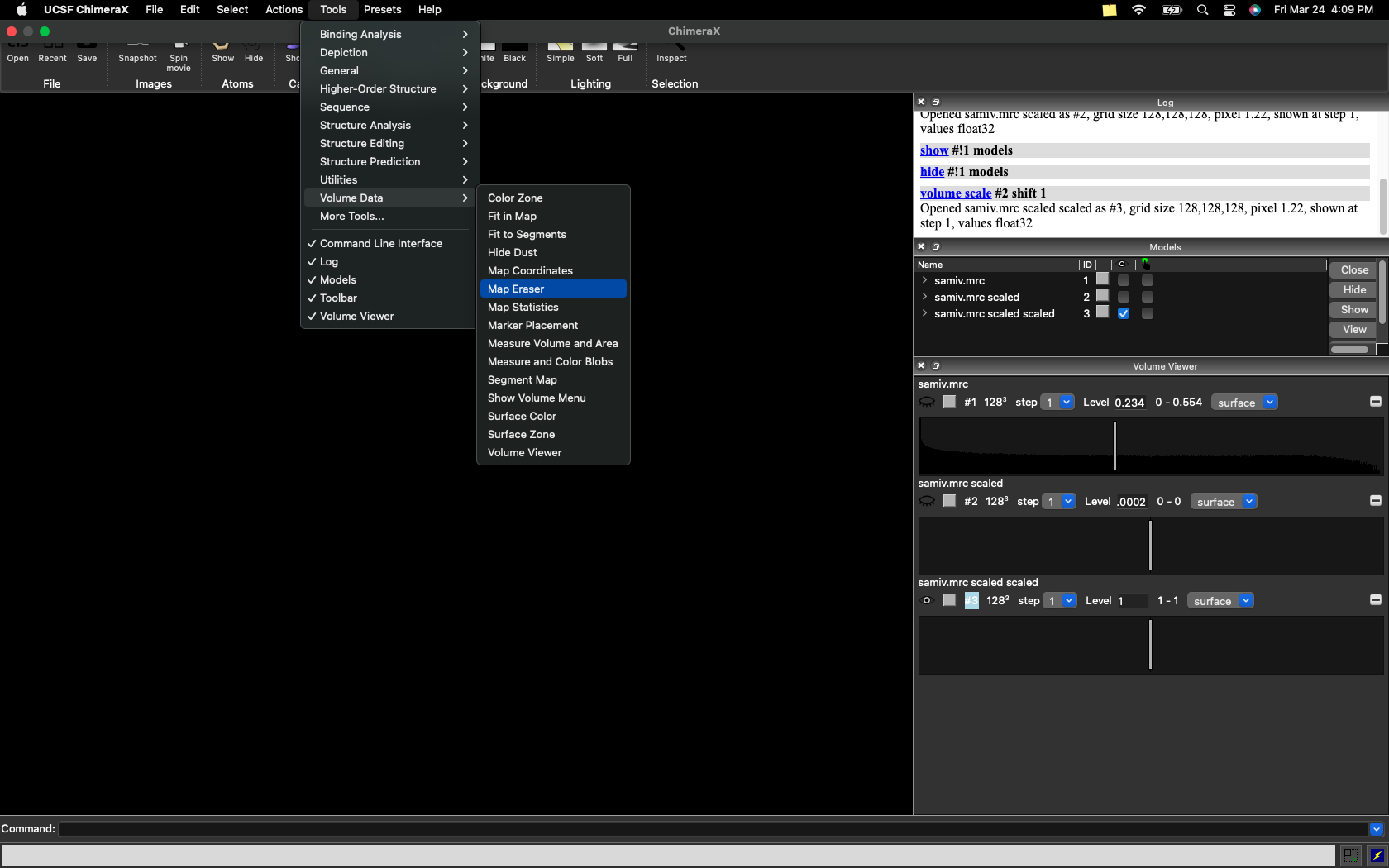
Now, reopen your Ab Initio volume and use the sliding scale of the map eraser to adjust the radius of the sphere to your desired size.
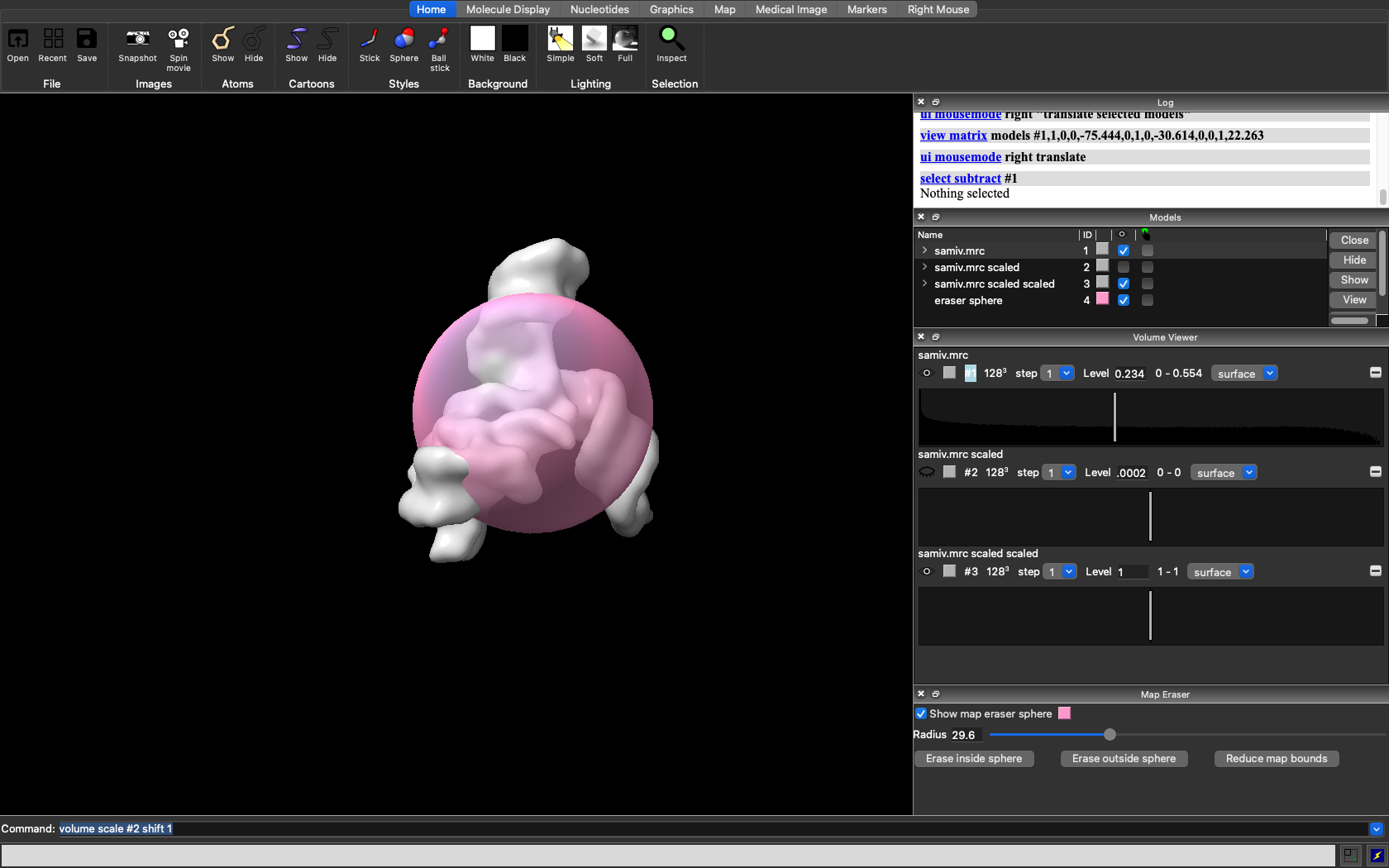
Now, deselect your Ab Initio volume, but make sure to leave map3 selected. Then click “Erase outside of sphere”. This will create a fourth and final volume which will contain the sphere of your desired size. To view it, scroll down to the newest volume and adjust the density bar so that you can view the sphere.
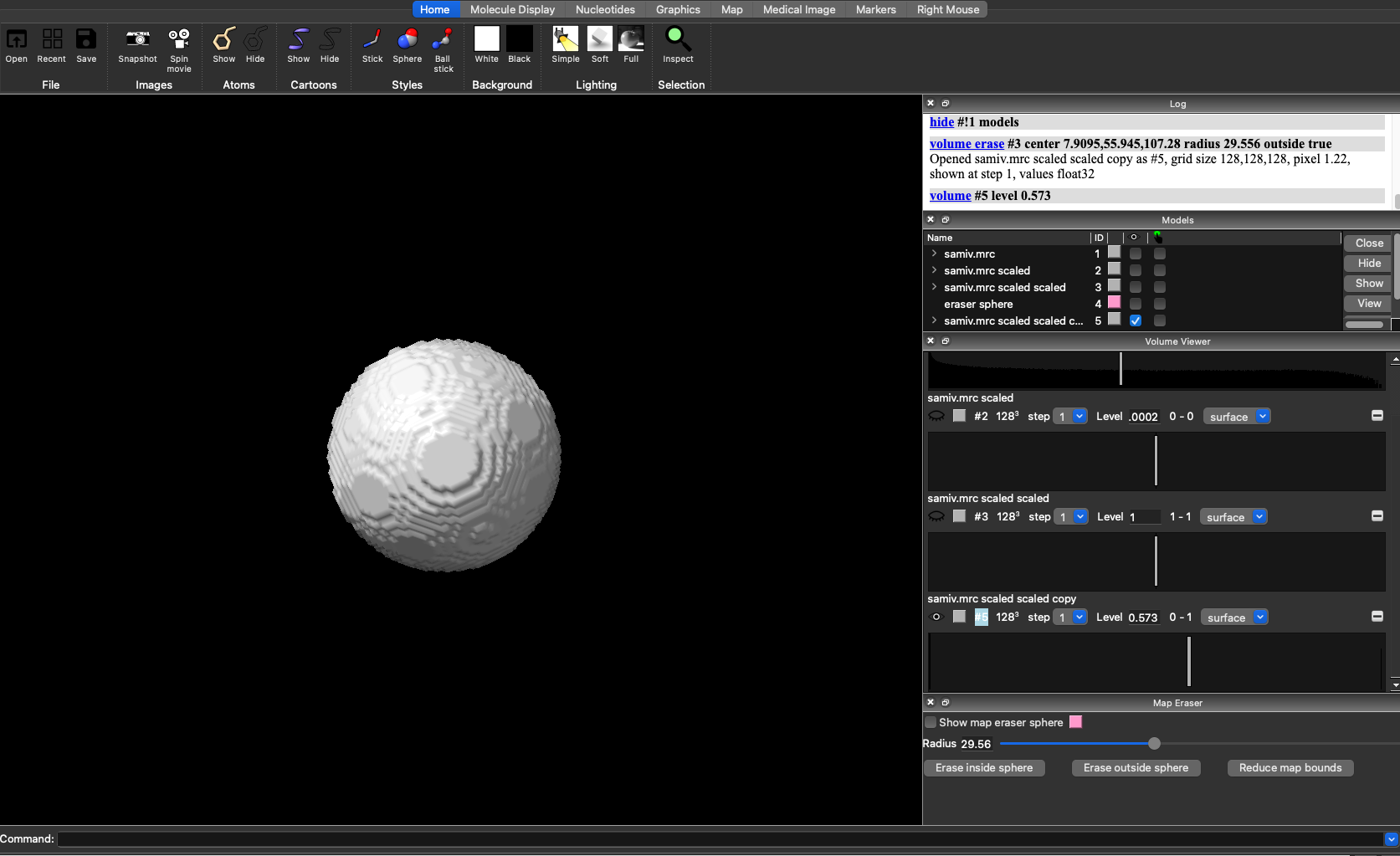
To save your volume, choose “Save” in the upper left corner. Make sure to change the “Files of type” option to MRC density map, and under “Map” select the newest volume with your sphere, which should have “scaled scaled copy” at the end of its name.
You can then import this sphere to Cryosparc to use in Heterogeneous classification using the “Import 3D Volumes” job and specifying the path to the volume.
